Police have detained 200 protesters following Tuesday’s deadly violence in India’s capital Delhi during a massive protest against agricultural reforms.
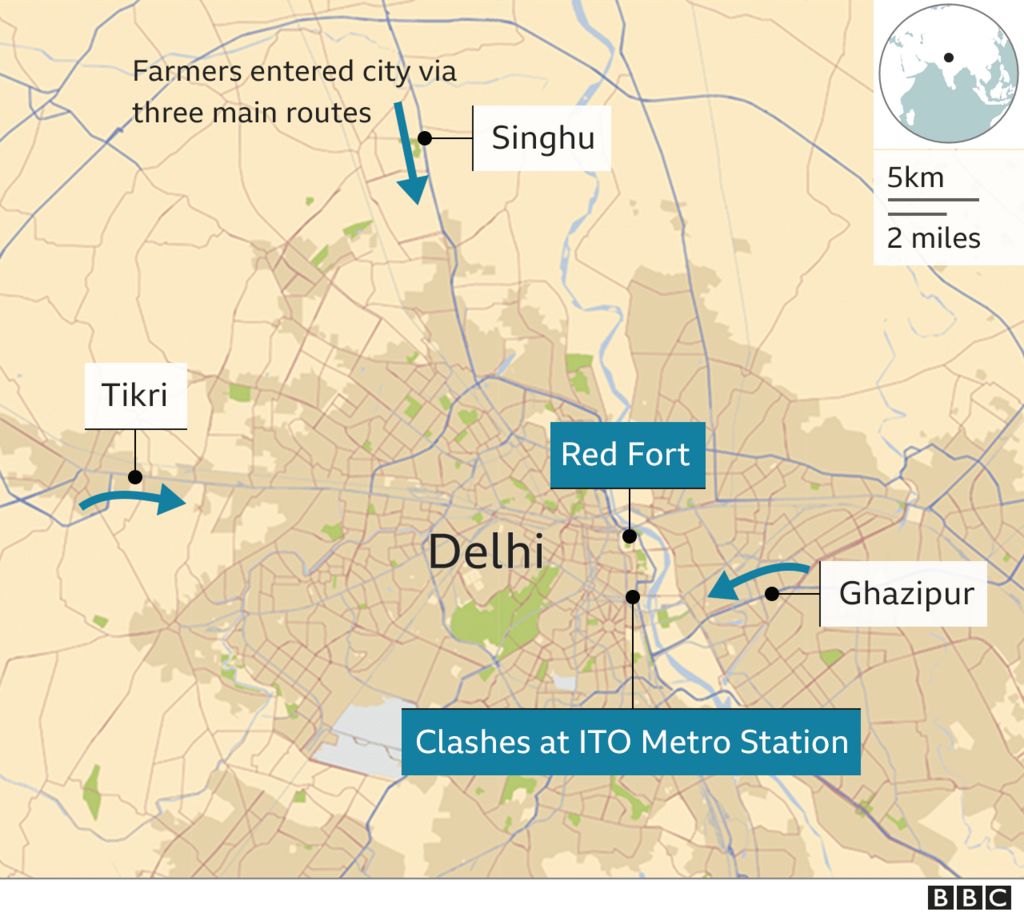
Thousands of farmers clashed with police as protesters on the outskirts of the city forced their way in.
One protester died, and more than 300 police officers were injured.
Blaming the chaos on rogue elements among an otherwise peaceful march, most farmers’ leaders said they would not call off their protests.
Those detained are being held on charges of rioting, damaging public property, and attacking police personnel. So far, 22 police complaints have been registered.
“We are making arrests after conducting proper verification. We are also looking into CCTVs near Red Fort, ITO, Nangloi and other areas where the violence erupted,” police officials told the Indian Express newspaper.
India’s government deployed 15 companies of paramilitaries to boost security after the protests, which also saw some farmers storming the city’s historic Red Fort and occupying the ramparts until police drove them out.
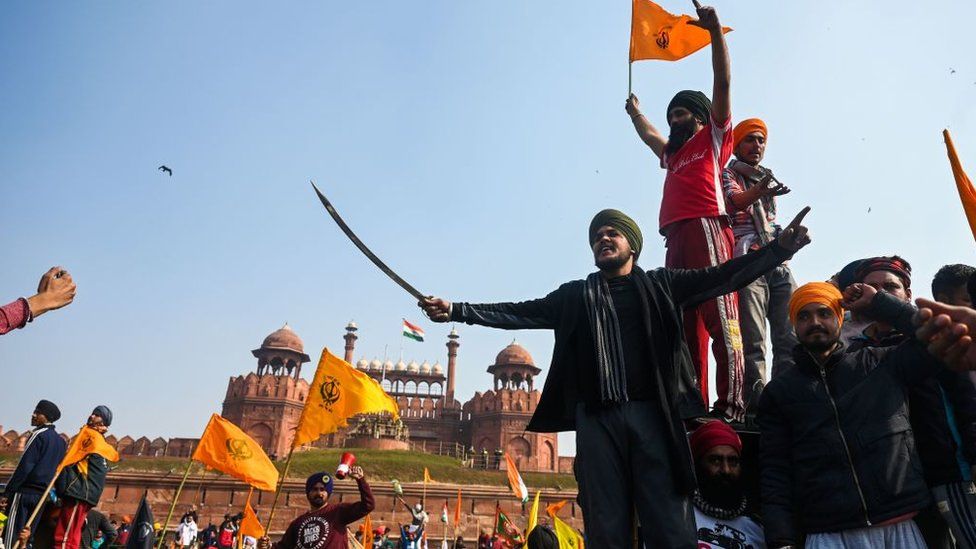
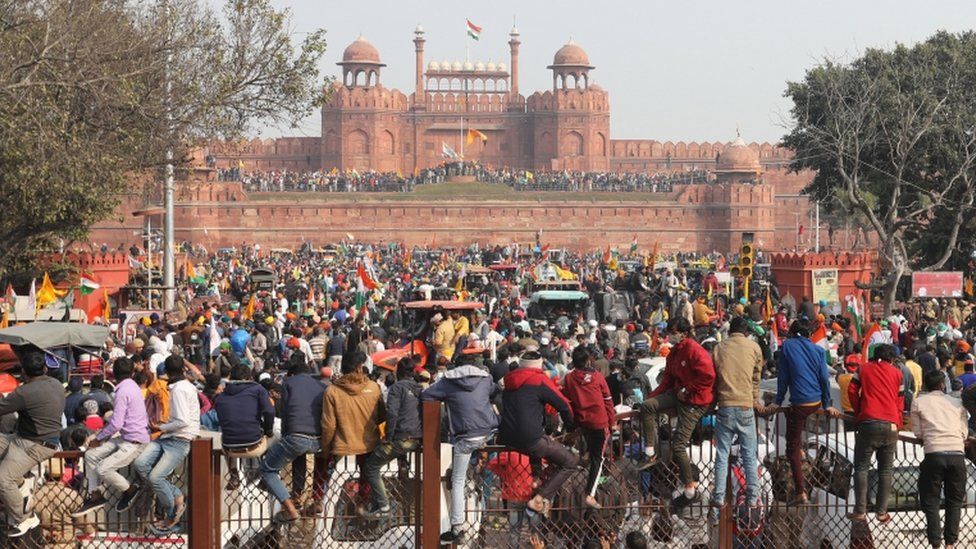


The violence coincided with Republic Day – a national holiday that marks the anniversary of India officially adopting its constitution on 26 January 1950.
Samyukta Kisan Morcha, an umbrella group of protesting farmers, said in a statement that they “condemn and regret the undesirable and unacceptable events and dissociate ourselves from those indulging in such acts”.
Two farmers’ unions withdrew from the ongoing agitation on Wednesday, but most said they were determined to continue their protests against the new agricultural laws.
The government says its reforms will liberalise the sector, but farmers say they will be poorer as a result.
Tens of thousands of them have been striking on the outskirts of Delhi since November, demanding that the laws be repealed. Last week they rejected a government offer to put the changes on hold.
How did the violence unfold?
The government had opposed the planned rally by farmers, but police allowed it on the condition that it would not interrupt the Republic Day parade in central Delhi.
Farmers were given specific routes for the tractor rally, which would largely be confined to the outskirts.
But shortly after the parade came to a close, convoys of tractors broke through police barricades and converged on the city centre. One group of protesters burst through security at the historic Red Fort where they clambered on to the walls and domes of the fortress, even hoisting flags alongside the national flag.
By Tuesday afternoon, police said they had removed protesters from the complex.
Some of the most violent clashes took place near the ITO metro station junction – on the route to central Delhi. Footage showed farmers attacking police with sticks and metal bars while officers used tear gas and batons.
Police said one protester died at the junction when his tractor overturned after hitting a barricade.

Police said in a statement that they had acted after farmers broke conditions for the rally and took “the path of violence and destruction”.
But one farmers’ union leader accused the police of provoking the violence.
“When you attack a peaceful protest, then difficulties for the government will surely increase,” Kawalpreet Singh Pannu told AFP news agency.
“This won’t stop here. Our movement and message have only become stronger.”

What is the Red Fort?
- The huge citadel, with its distinctive red sandstone walls, was built in the early 17th Century by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan and was the seat of Mughal rule until 1857, when India began to be governed by the British
- India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru hoisted the national flag from the fort on 16 August 1947 – a day after independence from Britain was declared
- The fort was designated a Unesco World Heritage Site in 2007

What do the new farming laws propose?
The laws loosen rules around the sale, pricing and storage of farm produce which have protected India’s farmers from the free market for decades.
Farmers fear that the new laws will threaten decades-old concessions – such as assured prices – and weaken their bargaining power, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation by private companies.
While Mr Modi has defended them, the laws have been likened to a “death warrant” by farmer groups.
Most economists and experts agree that Indian agriculture desperately needs reform. But critics of the government say it failed to consult farmers before passing the laws.
This article first appeared on bbc.com
